
In the realm of science, new discoveries ignite curiosity, unlock the unknown, and uplift the world. But ever imagined what will happen if a scientist's discovery turns out disastrous for the world? Scary, right! 😨
We are talking about the famous scientist Oppenheimer whose moonshot project to build an atomic bomb in a top-secret lab led to the biggest destruction of all time. Atomic & nuclear bombs are powerful weapons that use nuclear reactions as their source of explosive energy.
These weapons were first developed during World War II and have been used only twice by the United States against Japan in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
In this article, let’s shed some light on whether the legendary scientist really regretted his nuclear creation, why he is the ‘Father of the Atomic Bomb’, the history of the atomic bomb, wars and many more.
Who was Oppenheimer?
 Source: Today in Science History
Source: Today in Science History
J. Robert Oppenheimer (1904-1967) was an American theoretical physicist & one of the leading scientists involved in the famous Manhattan Project, which developed the first atomic bomb. Oppenheimer was also the one who expressed deep remorse and concerns about the destructive power of nuclear weapons which he created.
His sentiments were well captured in his famous statement after witnessing the successful test of the first atomic bomb in 1945, wherein he quoted a verse (Chapter 11 Shloka 32) from the Bhagavad Gita, an ancient Hindu scripture, saying, "Now I have become Death, the destroyer of worlds."
History of Atomic Bombs
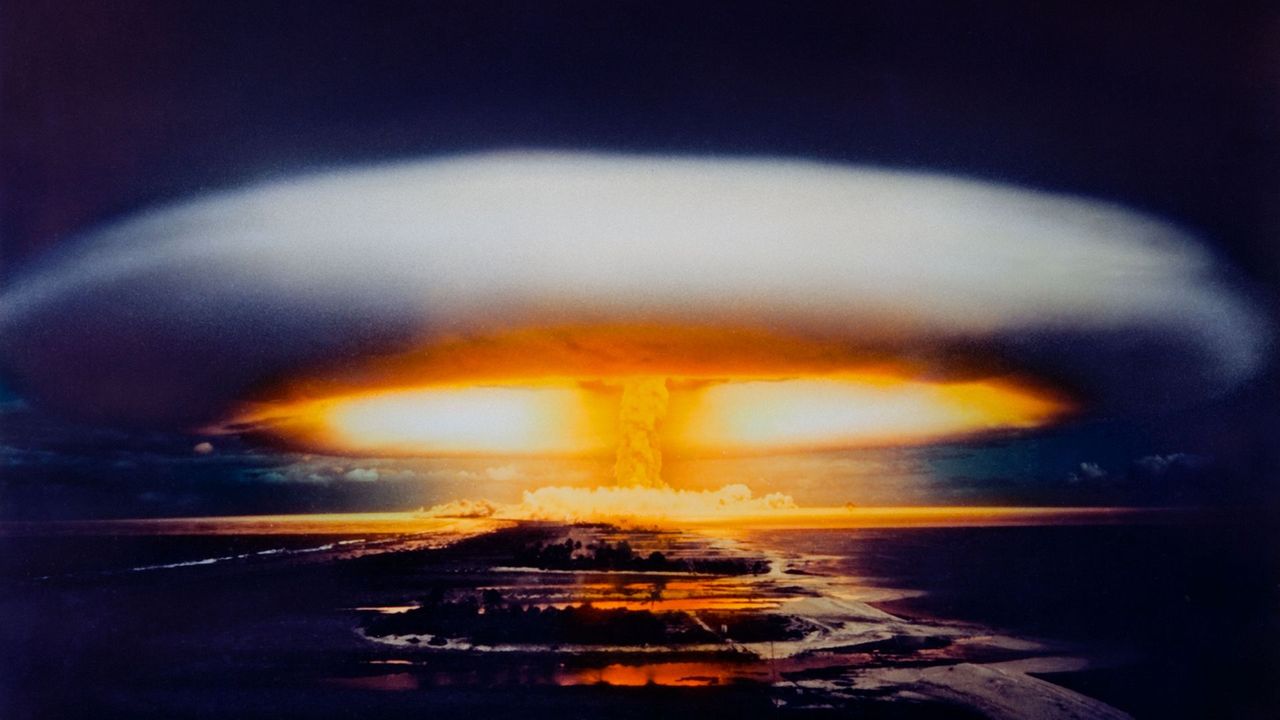 Source: BBC
Source: BBC
Atomic bombs are powerful weapons that use nuclear reactions as their source of energy. To date, it has only been used twice in a war by the United States against Japan, in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. A period of nuclear proliferation followed this war, and during the Cold War, the United States and the Soviet Union competed for supremacy in a global nuclear arms race.
Nuclear Bombs and Hydrogen Bombs
 Source: India Today
Source: India Today
- In 1938, a discovery by nuclear physicists in a laboratory in Berlin, Germany, made the creation of the first atomic bomb possible after Otto Hahn, Lise Meitner & Fritz Strassman discovered nuclear fission.
- What happens in nuclear fission is that the nucleus of an atom of radioactive material splits into 2 or more smaller nuclei, which generates a sudden & powerful release of energy.
- This discovery of nuclear fission opened the paths for creating nuclear technologies, including weapons.
- Hence, atomic bombs get their energy from fission reactions, whereas on the other hand, thermonuclear weapons, or hydrogen bombs, rely on a combination of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. (Nuclear fusion is another type of reaction in which two lighter atoms combine to release energy, the opposite of fission).
While discussing the history of hydrogen bombs or atomic bombs, how can we skip Manhattan Project?
Manhattan Project
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/scientists-visit-atomic-exhibit-515335876-5c6f614b46e0fb0001b681bb.jpg) Source: ThoughtCo
Source: ThoughtCo
In 1942, President Franklin D. Roosevelt authorised the Manhattan Project in order to gather various scientists and military officials for nuclear research.
- During World War II, Manhattan Project was the code name allotted for the American-led effort to develop a functional atomic bomb.
- The project was a response to fears that German scientists had been working on a weapon with the use of nuclear technology since the 1930s.
- Much of the work in the Manhattan Project was performed in Los Alamos, New Mexico, under the direction of J. Robert Oppenheimer, popularly known as the “Father of the atomic bomb.”
- In 1945, the Manhattan Project developed weapon was finally tested (the 1st successful atomic bomb explosion) at the Trinity test site in Alamogordo, New Mexico.
- However, by the time, this weapon was ready & tested, the Allies had already declared victory in Europe but were still fighting in Japan.
- Physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer, the laboratory director and the “Father of the atomic bomb,” watched from a distance that the bomb released a mushroom cloud 40,000 feet high.
- This is when he made his statement after witnessing the 1st atomic bomb test “Now I have become Death, the destroyer of worlds."
Now, let’s discuss the incidents when nuclear bombs were used in world history resulting in massive destruction.
Hiroshima and Nagasaki Bombings
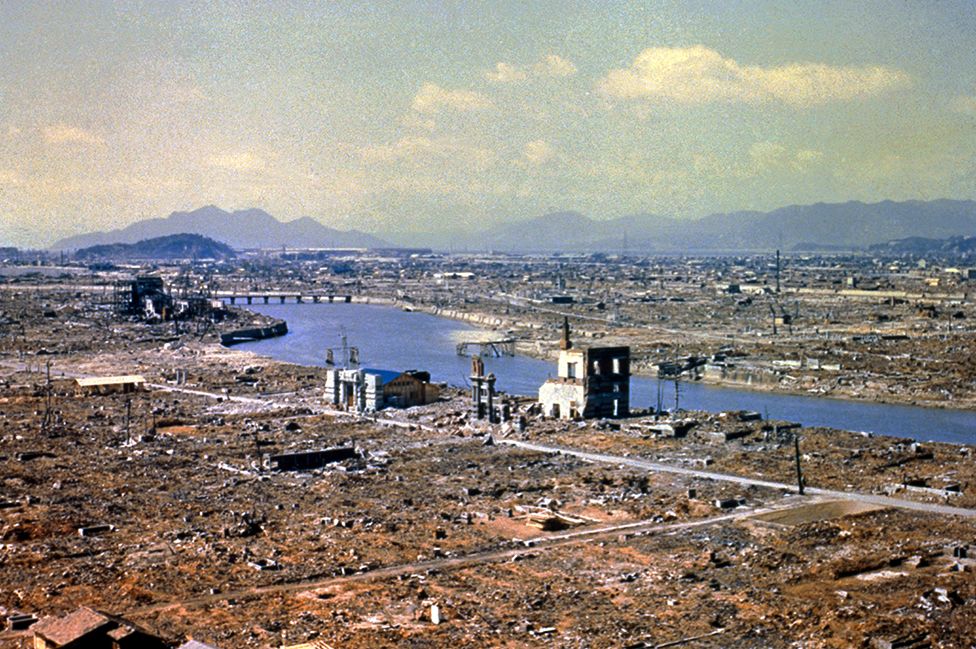 Source: BBC
Source: BBC
While World War II in Europe ended in April, yet fighting in the Pacific continued between Japanese forces and U.S. troops. Thus, motivating the US troops to drop the two atomic bombs in Japan. The two atomic bombs dropped in 1945 killed and maimed hundreds of thousands of people, and the horrifying effects are still being felt.
- Scientists at Los Alamos had developed two types of atomic bombs by 1945, a uranium-based design known as “the Little Boy” and a plutonium-based weapon known as “the Fat Man.” (Uranium and plutonium are both radioactive elements.)
- On August 6, 1945, the US dropped its first atomic bomb from a B-29 bomber plane called the Enola Gay over Hiroshima, Japan. The “Little Boy” exploded with about 13 kilotons of force, levelling five square miles of the city & killing 80,000 people instantly.
- When Japan did not immediately surrender, the US dropped a second atomic bomb three days later on the city of Nagasaki. The bomb named “Fat Man” killed an estimated 40,000 people on impact.
- Did you know? Nagasaki had not been the primary target for the second bomb. American bombers initially had targeted the city of Kokura, where Japan had one of its largest munitions plants.
- By the end of 1945, the bombing had killed around 140,000 people in Hiroshima and additionally 74,000 in Nagasaki.
- President Harry Truman called for Japan’s surrender with the Potsdam Declaration in late July. The declaration promised “prompt and utter destruction” if Japan did not surrender.
- Japanese Emperor Hirohito announced his country’s surrender on August 15, a day that became known as ‘V-J Day’, ending World War II.
- Even after all these years, many survivors face leukaemia, cancer, or other terrible side effects from radiation.
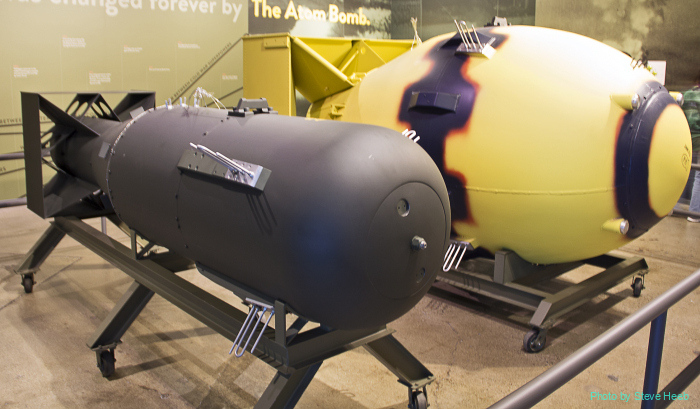 Little Boy & Fat Man Atomic Bombs
Little Boy & Fat Man Atomic Bombs
Source: Preserving our History
Long-term effects
It hardly takes 10 seconds for the fireball from a nuclear explosion to reach its maximum size, but the effects last for decades. After about a decade, survivors began suffering from thyroid, breast, lung and other cancers at higher than normal rates, leukaemia etc.
The Cold War
 Source: Encyclopedia Britannica
Source: Encyclopedia Britannica
The US was the only country with nuclear weaponry in the years immediately following World War II. The Soviet Union initially lacked the knowledge and raw materials to build nuclear warheads, however just within a few years, the U.S.S.R. had obtained, through a network of spies engaging in international espionage, blueprints of a fission-style bomb and discovered regional sources of uranium in Eastern Europe. Hence, in 1949, the Soviets tested their first nuclear bomb.
The United States responded by launching a program in 1950 to develop more advanced thermonuclear weapons. Finally, the deadly Cold War arms race began, and nuclear testing with research became a high-profile goal for many other countries, especially the United States and the Soviet Union.
What was the Non- Proliferation Treaty (NPT)?
Date of adoption: 12 June 1968
Place of adoption: United Nations, New York
Date of entry into force: 5 March 1970
Depositary Governments: Russian Federation, United Kingdom, United States
The NPT aims to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, foster the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and reach the goal of disarmament. The Treaty establishes a safeguards system under the responsibility of the IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency), which also plays a central role under the Treaty in areas of technology transfer for peaceful purposes.
The NPT contains 11 articles that apply to both nuclear-weapon States parties and non-nuclear-weapon States parties promoting cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy. By signing and adhering to the treaty, countries gain legitimacy and recognition from the international community as responsible actors committed to non-proliferation.
Is India a member of NPT?
No, India is not a member of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). India is one of the few countries known to possess nuclear weapons but has not signed the NPT. Instead, India follows a policy of voluntary nuclear restraint & maintains a nuclear doctrine based on credible minimum deterrence. That is, India has a "no-first-use" policy, stating it will not be the first to use nuclear weapons in any conflict.
Illegal Nuclear Weapon States
Five countries, such as the United States, Russia, China, France, and the United Kingdom, are recognized as nuclear-weapon states under the NPT, which entered into force in 1970. India, Pakistan, and Israel are known to possess nuclear weapons but have not signed the NPT.
North Korea withdrew from the NPT in 2003 and has since conducted nuclear tests, making it the only country to have openly tested nuclear weapons in the 21st century. North Korea tested two long-range intercontinental ballistic missiles in 2017, one reportedly capable of reaching the US mainland.
- Some countries wanted the option of developing their own nuclear weapons arsenal, so they never signed the NPT; they never wanted to get bound by any obligations of such treaties.
- India was the first country outside of the NPT to test a nuclear weapon in 1974, whereas Pakistan has a known nuclear weapons program. Israel is widely believed to possess nuclear weapons, though it has never officially confirmed or denied the existence of a nuclear weapons program. South Sudan is not known or believed to possess nuclear weapons.
Conclusion
Despite some close calls, no country has used nuclear bombs as weapons since the disastrous incidents of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. This means that, by far, we’ve been able to avoid the nuclear future Oppenheimer feared he’d already set in motion. Undoubtedly, international cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy, including nuclear research, medical applications, and nuclear power generation, will continue to evolve so that Hiroshima and Nagasaki incidents are never repeated.
FAQs on Atomic Bomb and the Father of Atomic Bomb
- Question: Who is often referred to as the "father of the atomic bomb"?
Answer: J. Robert Oppenheimer.
- Question: Which scientific research project led to the development of the atomic bomb during World War II?
Answer: The Manhattan Project.
- Question: In which year was the first atomic bomb test conducted as part of the Manhattan Project?
Answer: The first atomic bomb test, codenamed Trinity, was conducted on July 16, 1945.
- Question: What was the code name of the first atomic bomb test conducted at the Trinity Site in New Mexico?
Answer: Trinity.
- Question: Which famous physicist directed the Los Alamos Laboratory and played a key role in the development of the atomic bomb?
Answer: J. Robert Oppenheimer.
- Question: What famous quote is associated with J. Robert Oppenheimer upon witnessing the first atomic bomb test?
Answer: "Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds."
- Question: Which two cities in Japan were targeted with atomic bombs during World War II?
Answer: Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- Question: What were the code names of the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki?
Answer: The code name of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima was "Little Boy," and the one dropped on Nagasaki was "Fat Man."
- Question: Which country became the first to develop and test a nuclear weapon following World War II?
Answer: The United States.
- Question: Which international organization works to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promotes the peaceful use of nuclear energy?
Answer: The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
What are your views on the upcoming movie “Oppenheimer”? Is it possible to have a nuclear-free world ahead in future?
Comment down your views!😅